Literature genres function as navigational cues, directing readers to search for narratives corresponding to their inclinations and areas of interest. Although romance, science fiction, and mystery novels frequently garner more attention, an additional classification subtly yet effectively commands attention: men’s fiction. Men’s fiction comprises a wide range of narratives exploring masculinity’s intricacies, providing valuable perspectives on the male psyche, experiences, and emotions. Despite being frequently misunderstood and overlooked, it incorporates diverse themes. Gay books have made a notable contribution to the genre by providing various viewpoints on masculine identities and relationships. In this exploration, we venture into the heart of men’s fiction, unraveling its essence, evolution, and significance in contemporary literature, focusing on gay books as a pivotal part of this narrative landscape.
Defining Men’s Fiction
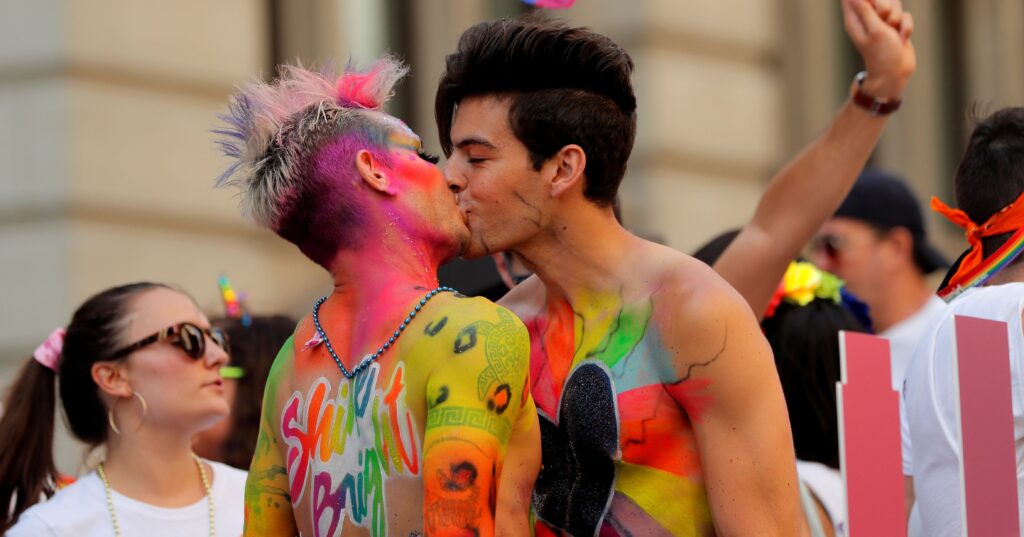
Men’s fiction, fundamentally, comprises narratives that center on male protagonists, their trials, tribulations, and connections. This literary genre encompasses many themes and tones, including the diverse array of gay books, which delve into introspective narratives that examine vulnerability and personal development, as well as grim tales of survival and adventure.
An inquiry that may arise is what sets men’s fiction apart from other literary genres. Its defining characteristic is its exploration of masculinity in all its facets, including the diversity of masculine experiences highlighted in gay books.
Themes and Motifs
Specific themes and motifs resurface in men’s fiction, striking a chord with readers and serving as a reflection of masculinity’s complex and multifaceted essence. The following themes are encompassed:
Identity and Self-Discovery:
Numerous works of men’s fiction feature protagonists who confront issues of identity and self-realization as they negotiate the complexities of their selves and societal expectations. These narratives, which range from coming-of-age stories set in adolescence to midlife crises examining existential anxiety, provide thought-provoking contemplations on the contemporary male experience.
Brotherhood and Camaraderie:
Establishing connections among male characters, whether using common hardships, triumphs, or shared experiences, constitutes a primary motif in men’s fiction. The narratives above exalt the potency of companionship and friendship, underscoring the criticality of solidarity and reciprocal assistance when confronted with hardship.
Conflict and Resilience:
Men’s fiction frequently examines conflict and resiliency, constantly encompassing interior struggles against personal demons and epic battles on the battlefield. Protagonists undergo rigorous testing, wherein their resolve and ability to confront external adversaries or internal turmoil are forged in the crucible of adversity.
Love and Relationships:
Although romance and intimacy may not always be the primary focus of men’s fiction, these narratives frequently explore these themes. These narratives provide nuanced depictions of masculine emotions and relationships, whether intertwined with familial ties, friendships, or romantic entanglements.
Evolution of Men’s Fiction


Men’s fiction has evolved to embrace more diverse and inclusive storytelling, with gay books playing a significant role in this transformation. These works challenge stereotypes and offer diverse narratives that reflect a broader range of male experiences and identities.
From Stereotypes to Complexity:
Historically, men’s fiction frequently reinforced preconceived notions of masculinity through its depictions of male protagonists as emotionally immature stoics or indomitable champions. On the contrary, these stereotypes have been progressively confronted by contemporary authors who created characters with substance, complexity, and vulnerability. Modern men’s fiction encompasses a more nuanced comprehension of masculinity, delving into gender fluidity, non-traditional family structures, and introspective examinations of fatherhood and masculinity.
Diversity and Representation:
In response to society’s increasing diversity and inclusivity, men’s fiction has expanded its scope to encompass a wider array of experiences and perspectives. Literary works from marginalized communities, such as those written by men of color, LGBTQ+ individuals, and men with disabilities, have contributed to the genre’s complex tapestry of representations and narratives. These narratives provide readers with a more reflective and inclusive depiction of masculinity, challenging conventional stories and expanding the genre’s readership.
Blurring Genre Boundaries
Men’s fiction, including gay books, often intersects with other literary genres, defying easy classification. This hybrid nature encourages readers to expand their understanding of what men’s fiction—and gay books—can be.
The Significance of Men’s Fiction
Men’s fiction, with gay books as a vital component, plays a crucial role in shaping conversations about masculinity and male experiences. By offering diverse narratives, these books foster empathy, encourage self-reflection, and inspire dialogue and change, contributing to a more inclusive and understanding society.
Fostering Empathy and Understanding:
Men’s fiction employs nuanced characterizations and immersive narratives to beckon readers into the personal lives of its male protagonists, thereby promoting gender-neutral empathy and comprehension. Through active participation in narratives that question conventional ideas of masculinity and emphasize the common humanity of every person, readers are prompted to examine their prejudices and preconceived notions, ultimately cultivating a deeper sense of compassion and unity.
Promoting Self-Reflection and Development:
Men’s fiction, specifically, provides an avenue for male readers to engage in introspection and self-reflection by presenting storylines that connect with their personal challenges, vulnerabilities, and ambitions. Through exploring identity, relationships, and personal development, the text prompts readers to contemplate their experiences and convictions, cultivating a more profound comprehension of one’s being and societal position.
Inspiring Dialogue and Change:
As men’s fiction progresses and becomes more varied, it can stimulate substantive discourse and societal transformation. By activating underrepresented individuals, questioning preconceived notions, and examining the intricate nature of masculinity, these narratives foster more extensive dialogues concerning social justice, gender parity, and representation. Through literary works, readers are encouraged to consider alternative conceptions of masculine identity and relationships, thereby fostering the development of a more compassionate and inclusive society.
Conclusion
Men’s fiction presents a wide range of narratives that delve into the intricacies of masculinity; gay books, in particular, offer a critical outlook on masculine identities and relationships. The genre’s ongoing development encourages readers to delve into every aspect of the male experience, thereby cultivating a more profound comprehension and admiration for the wide array of male lives and romantic relationships.